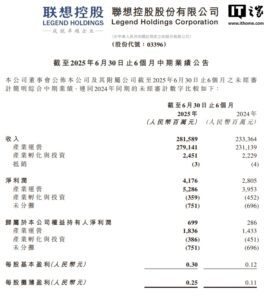
7月12日,北京,国家发改委发布《关于促进绿色消费的指导意见》
快速阅读: 北约E-3预警机在波兰空域监测俄乌冲突,初期俄战机频繁轰炸,现多采用远程导弹和无人机攻击,双方空中活动减少,战场转向静态消耗战。
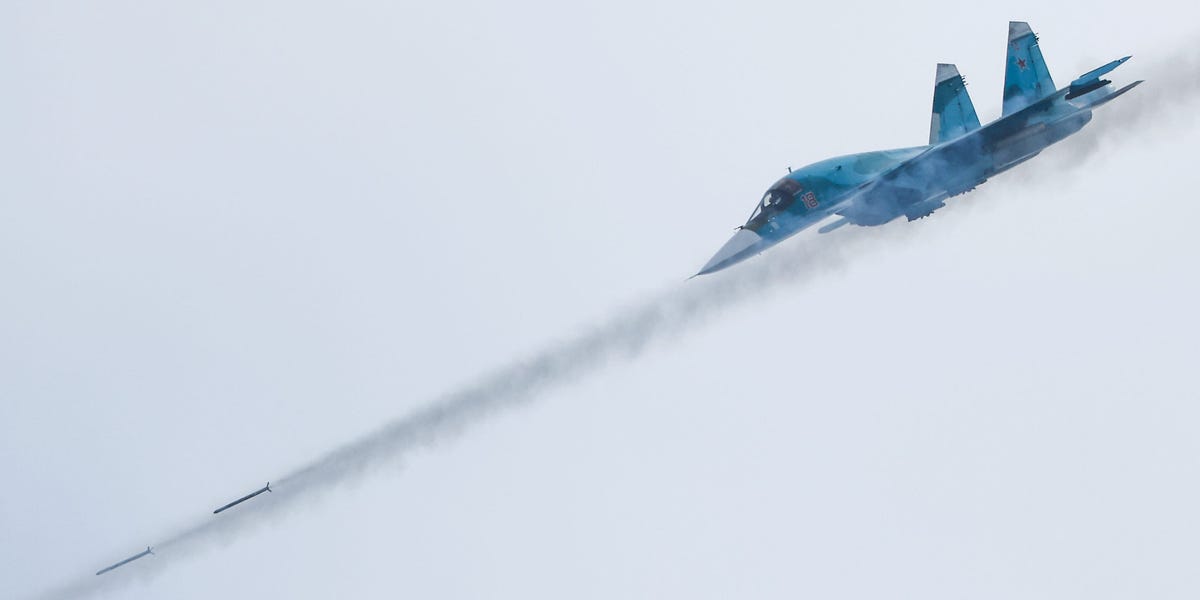
IN POLISH AIRSPACE — The crew of this NATO surveillance aircraft may not be able to see every detail of the fighting in Ukraine from its cruising altitude of 30,000 feet, but they still have a surprisingly clear picture of the battlefield.
From high above Eastern Europe, NATO’s airborne surveillance crews operating the alliance’s
E-3 Sentry planes
have tracked Russia’s evolving air war since the start of its full-scale invasion of Ukraine.
In the early days, aircrews watched Russian warplanes fly bombing runs toward the front lines. Now, aircraft are rarely crossing into Ukrainian airspace, having largely been replaced by standoff missile strikes and drone attacks as both sides rely more on
air defenses
and long-range firepower.
At the beginning of the war, “you saw a lot of activity.” Capt. Jasper, a Dutch surveillance controller who monitors the airspace and surface, told Business Insider aboard the E-3 during a recent mission over Eastern Europe in support of NATO’s
Baltic Sentry
operation.
But as the front lines gradually froze and the war became more static, there was “less activity with airplanes,” he said. “That’s actually what we saw on our side.”
Russian jets and helicopters were common air assets early in the war.
DIMITAR DILKOFF via Getty Images
In the early weeks of the invasion, Russian
jets and helicopters
were commonly seen in Ukrainian skies, flying deep into the country to support advancing forces, though often inadequately. But losses and effective Ukrainian air defenses, which Russia
failed to suppress
, blunted its efforts.
The war moved east, where Russia could
lob missiles into Ukraine
or let its bombers fire from relative safety. Both sides fielded air defenses so thick that the NATO aircrews watching from high above could see the shift — pilots on both sides stopped flying into range, and Russia’s air war became increasingly remote.
Related stories
Business Insider tells the innovative stories you want to know
Business Insider tells the innovative stories you want to know
The skies over Ukraine have become a battlefield defined by denial, not air dominance. Neither side owns the skies, so Russia and Ukraine punish the enemy from a distance. And the E-3 surveillance crews have seen the difference.
NATO’s eyes in the sky
The E-3, a modified
Boeing
707/320 passenger jet, can detect hostile aircraft, ships, and missile launchers from far away. It has a 360-degree rotating radar dome that can see over 300 miles across the air and surface, and high-tech sensors that, unlike ground stations, are not restricted by terrain or the Earth’s curvature.
NATO’s E-3 fleet has been tracking the war in Ukraine.
US Air Force Staff Sgt. Andrew D. Sarver
The airborne warning and control system, or
AWACS
, can also track friendly assets and interface with them. Data collected by the plane can be easily distributed in real time to
NATO
aircraft, ships, or command centers, giving allies critical situational awareness during war or peacetime.
NATO received its first E-3 in the early 1980s, and the small-but-capable fleet has flown in support of numerous missions and conflict operations in the decades since, including over North America, Europe, and the Middle East.
Russia’s illegal annexation of Crimea in 2014 marked a turning point for the AWACS fleet, which began to see increased activity in Eastern Europe. After Moscow’s
full-scale invasion of Ukraine
in 2022, NATO intensified its air patrols to better monitor Russian activities and deter any aggression on the alliance’s eastern flank.
Maj. Ben, an American officer and the E-3’s fighter allocator in charge of coordinating with other aircraft, said NATO’s air policing missions in Eastern Europe have gone from sporadic to regular since 2022.
“We fly more — provide more deterrence,” explained Maj. Ben, who, like other members of the multinational crew that BI spoke with during the flight, could only be identified by his rank and first name for security reasons.
The E-3 doesn’t carry weapons, but it provides situational awareness, coordination, and visibility that extend the alliance’s radar horizon by hundreds of miles and make it harder for an adversary to hide movements or attempt surprise attacks, boosting deterrence.
Russia has used highly destructive glide bombs to strike Ukrainian military positions and civilian areas.
Russian Defense Ministry Press Service via AP, File
The AWACS fleet is also tracking how the battlefield has changed in Ukraine. Capt. Jasper said airpower was a heavy feature at the start of the full-scale invasion, but this slowed down as the war shifted from maneuver-heavy combat to a more
attritional campaign
, and the front lines became more static.
“What we see is more ISR flights — surveillance and reconnaissance flights — and not as much air activity into Ukraine anymore,” he explained, and recalled how the crew could watch on their computer screens as aircraft took off, flew toward the
front lines
, and turned away — signalling that a bombing run had ended.
Capt. Donny Demmers, a Dutch public affairs officer who was permitted to share his full name, said aircraft avoid getting too close to the front lines now because Ukraine and Russia are both fielding sophisticated air defense systems that threaten enemy jets.
“But you still see there will be a lot of missile attacks,” he explained. However, instead of close bombing runs, the attacks are carried out at longer ranges using standoff weapons.
Ukrainian officials, including
President Volodymyr Zelenskyy
, have constantly pushed Kyiv’s Western military backers for additional
air defense systems
and ammunition to replenish exhausted stockpiles amid Russia’s worsening missile and drone attacks on major cities.
(以上内容均由Ai生成)